A Primer on Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids:
Millions of people worldwide face hearing loss, a common condition that hampers effective communication and enjoyment of daily activities. Until last year, the only recourse for these individuals was to buy professionally fitted hearing aids with prescriptions and fittings from a licensed audiologist. Now, they can purchase over-the-counter hearing aids designed for mild to moderate hearing loss. This article explains over-the-counter hearing aids, their working, their pros, and cons compared to professionally fitted devices, choosing the right size and type, acclimatization tips for a new device, typical problems with over-the-counter hearing aids, and essential maintenance tips to keep the device in good condition.
Understanding Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids and Their Working:
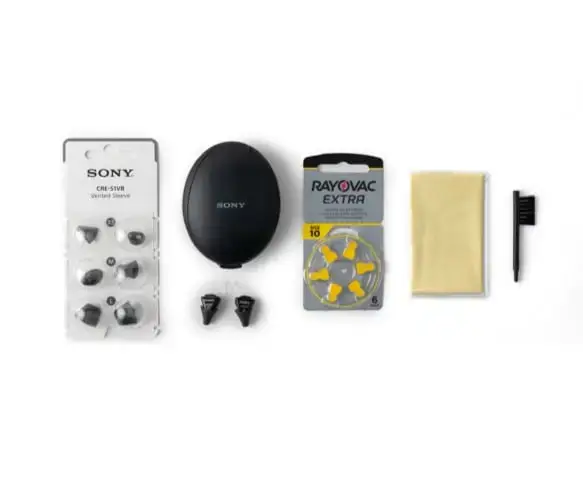
Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids, pre-programmed for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss, are typically smaller, less expensive, and easier to acquire than professionally fitted devices. Like traditional hearing aids, they use tiny microphones to capture, amplify, and deliver sound to the ear, often featuring adjustable volume controls for different sound environments.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of Over-The-Counter Hearing Aids:
The cost savings of OTC hearing aids is a significant advantage. Being less expensive and readily available without prescriptions or fittings, they may serve as a feasible option for people who cannot afford traditional hearing aids. However, OTC hearing aids might not effectively serve users with severe hearing loss or complex hearing needs. And unlike professional audiologists, OTC hearing aids can’t offer personalized adjustments and counseling services.
Choosing the Right Size and Type of Hearing Aid:
Consulting a professional audiologist is crucial to select the right type of hearing aid. They can evaluate your hearing needs and help determine the suitable type and size of hearing aid. If opting for an OTC device, ensure its size and shape fit comfortably in your ear. Some OTC devices offer customization for your specific needs through online hearing tests.
Tips for Acclimating to Your New Device:
Adjusting to a hearing aid takes time, so be patient. Gradually extend usage time each day until you comfortably wear the hearing aid all day. Remember, hearing aids don’t cure hearing loss, so keep your expectations realistic. Practice good communication habits by speaking clearly, facing the person you’re talking to, and asking them to speak louder if necessary.
Common Issues with Over-The-Counter Hearing Aids:
OTC hearing aids may have issues like poor sound quality, difficulty in speech recognition, discomfort due to ill-fitting devices, difficulty with background noise, feedback, earwax buildup, and dead batteries.
Maintenance Tips to Keep Your Device in Good Condition:
Regular maintenance is crucial for the device’s proper function. Clean your hearing aid daily with a soft, dry cloth, avoid water that can damage the device, regularly remove earwax buildup from the earpiece, and store batteries in a cool, dry place.
Over-the-counter hearing aids serve as an excellent option for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss, given their lower costs and greater availability compared to professionally fitted devices. But they may not suit those with complex needs. Those considering OTC hearing aids should consult an audiologist, choose the right device, practice good communication habits, and properly maintain the device. So, weigh the pros and cons before making your final decision. At Hears Hearing & Hearables, we’re ready to assist with your decision. Call us now.